How Do URL Shorteners Work?
A deep dive into the technology behind URL shorteners, from simple redirects to complex analytics and security features.
Published on July 10, 2024
URL shorteners are truly amazing tools. You give them a long, messy web address. They hand you back a neat, short link. It feels like pure magic. But what's really going on? It’s a simple, yet clever, system. Databases and web redirects power this magic. Think about a very long web address.
It might look like this: www.anothersite.com/categories/products/specific-item/more-details?id=12345&type=new. This long link is hard to share. It's prone to errors when typed. That's where URL shorteners come in. They take that lengthy address and transform it. They generate a much shorter version, like bit.ly/abcde. Behind this transformation is a powerful database. This database acts like a digital address book. It stores pairs of information. One part is the long, original URL. The other part is the new, short URL. When you create a short link, the service adds this pair to its database.
So, when someone clicks your short link, say bit.ly/abcde, something happens fast. Their web browser sends a request. It asks the URL shortening service for the destination. The service quickly looks up bit.ly/abcde in its database. It finds the original, long URL that is linked to it. Then, it tells your browser where to go. This telling is called a web redirect. It's like a polite nudge. The service tells your browser, "Hey, that short link you clicked? Go to this other, longer address instead." Your browser then automatically follows that instruction. It takes you to the intended website.
This whole process happens in the blink of an eye. You rarely even notice it. It makes sharing links much easier. It cleans up your messages and posts.
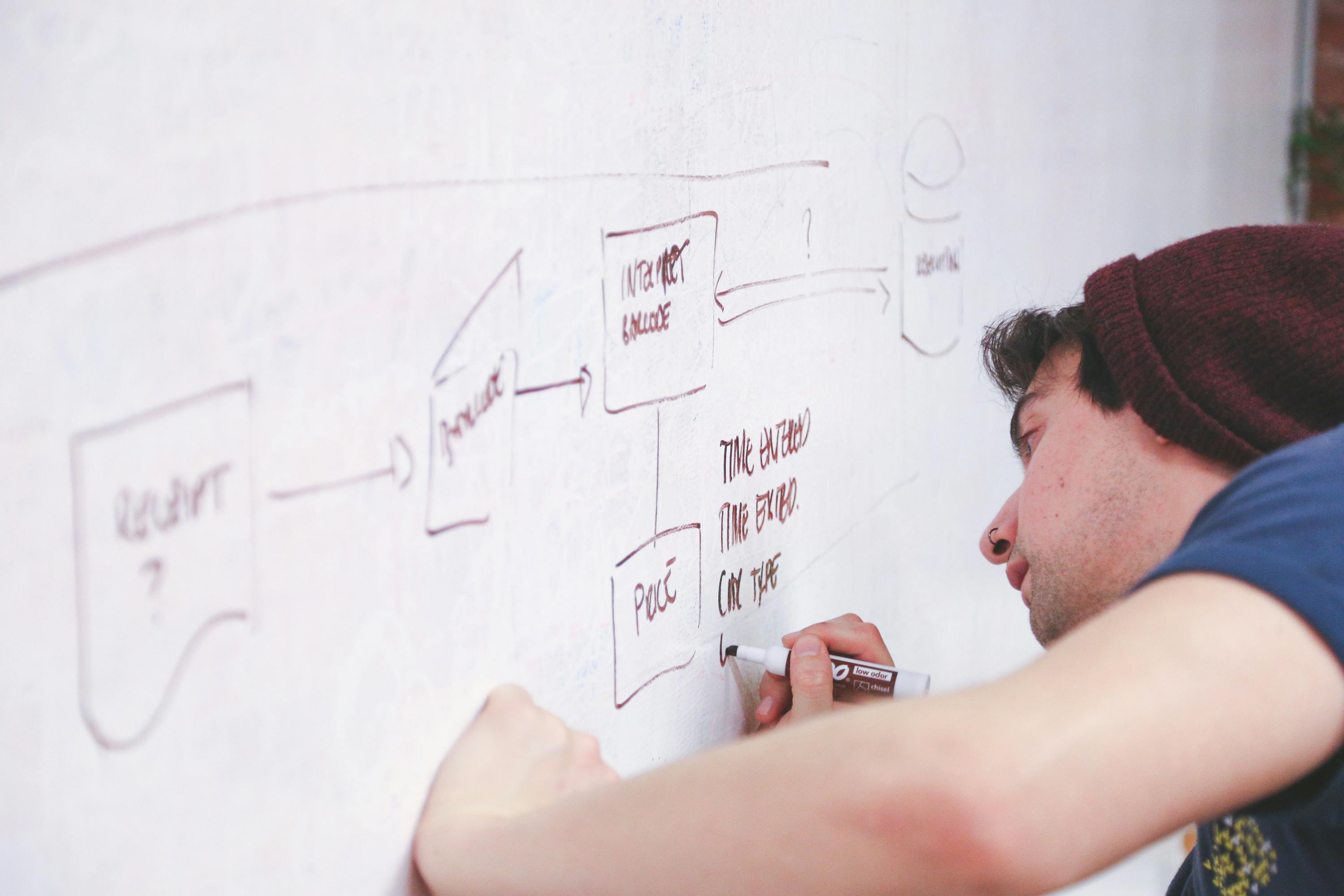
The Core Concept: A Digital Address Book
At its core, a URL shortener functions as a vast digital directory. When a user submits a lengthy web address, the servic performs two fundamental actions to facilitate easier sharing and management of these links.
- It meticulously crafts a unique, abbreviated string of characters. This string typically consists of a mix of letters and numbers, for instance,
bx7R9p. This distinct sequence is then designated as the "shortcode." This shortcode is designed to be memorable and concise, a stark contrast to the often unwieldy original address. - The service establishes a persistent connection between the original, extended URL and the newly generated shortcode. This pairing is securely recorded within the service's database. The shortcode serves as a unique identifier, acting as a key. The long URL, the original destination, is stored as the corresponding value associated with that key. This organizational structure is crucial for the service's operation. When someone uses the shortcode, the system retrieves the paired long URL, directing the user to the intended web page.
This process streamlines link sharing, making it more manageable across various platforms and communications
The Redirect Process
When someone clicks your new short link (e.g., `mnfy.in/a1b2C3d`), their browser sends a request to the URL shortener's server. The server then:
- Receives the request and extracts the shortcode (`a1b2C3d`).
- Looks up this shortcode in its database to find the corresponding long URL.
- If found, it sends a "redirect" response back to the browser. This response includes the original long URL.
- The browser receives this redirect and automatically navigates to the long URL's destination.
This all happens in a fraction of a second, so the user experience is nearly seamless. The type of redirect used is typically a "301 Permanent Redirect," which tells search engines that the short link has permanently moved to the new address.
Beyond the Basics: Analytics and Features
Modern URL shorteners introduce extra steps. This enhances their functionality. The service gathers data before sending you to the final link. They record details about your request. This includes the exact time you clicked. They also note your general location. This is figured out from your IP address. Information about the website you came from is also logged.
This is the source of their click analytics. These analytics show how popular a link is. They reveal where clicks originate. This data helps users track campaign success. URL shorteners also perform crucial checks. They verify that the shortened link is still active. They ensure the link has not expired. Additionally, they scan for malicious content. This protects users from harmful websites. Links on a blocklist are flagged. This prevents access to known threats. These added steps create a more robust system. They offer valuable insights and security.